 If you are experiencing earaches or partial hearing loss, the problem might be excessive ear wax buildup.
If you are experiencing earaches or partial hearing loss, the problem might be excessive ear wax buildup.
Ear wax serves an important purpose. It traps harmful bacteria and other small particles, preventing them from entering the ear. It also coats the skin of the ear and serves as a water repellant.
Everyone produces ear wax. It is produced by tiny hair follicles and glands in the ear canal. For most, the wax usually falls out on its own or while washing. For others however, the glands produce more ear wax than can be naturally removed. Those with smaller ear canals might also experience ear wax buildup because a narrower ear canal may have a more difficult time pushing the wax out. When this excess wax fails to fall out, it can harden in the ear canal and become impacted.
The misuse of cotton swabs greatly contribute to ear wax build-up because when used incorrectly, they push the ear wax deeper into the ear canal, causing a blockage. Hearing aids and ear buds can similarly cause ear wax impactions.
There are many symptoms of ear wax impaction, including:
- Dizziness
- Pain
- Plugged or fullness sensation
- Ringing in the ear (tinnitus)
- Partial & progressive hearing loss
In fact, wax blockage is one of the most common reasons for hearing loss
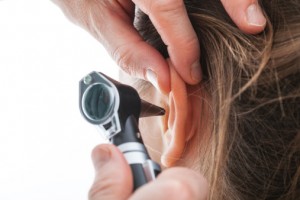
Blockage due to ear wax build-up is a ear problem doctors frequently see, affecting about 6% of all Americans, but it is easily treatable. A doctor can examine and diagnose ear wax buildup using an otoscope. There are a variety of over-the-counter drops designed to soften the wax. A bulb syringe can also be used to gently flush the ear with warm water. If these remedies don’t work, a doctor can suction the ear canal or remove impacted wax with a curette.
If left untreated, symptoms can worsen and lead to an infection. To make an appointment at Jamaica Hospital’s Audiology Center, please call 718-206-7110.
All content of this newsletter is intended for general information purposes only and is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Please consult a medical professional before adopting any of the suggestions on this page. You must never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment based upon any content of this newsletter. PROMPTLY CONSULT YOUR PHYSICIAN OR CALL 911 IF YOU BELIEVE YOU HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY.
