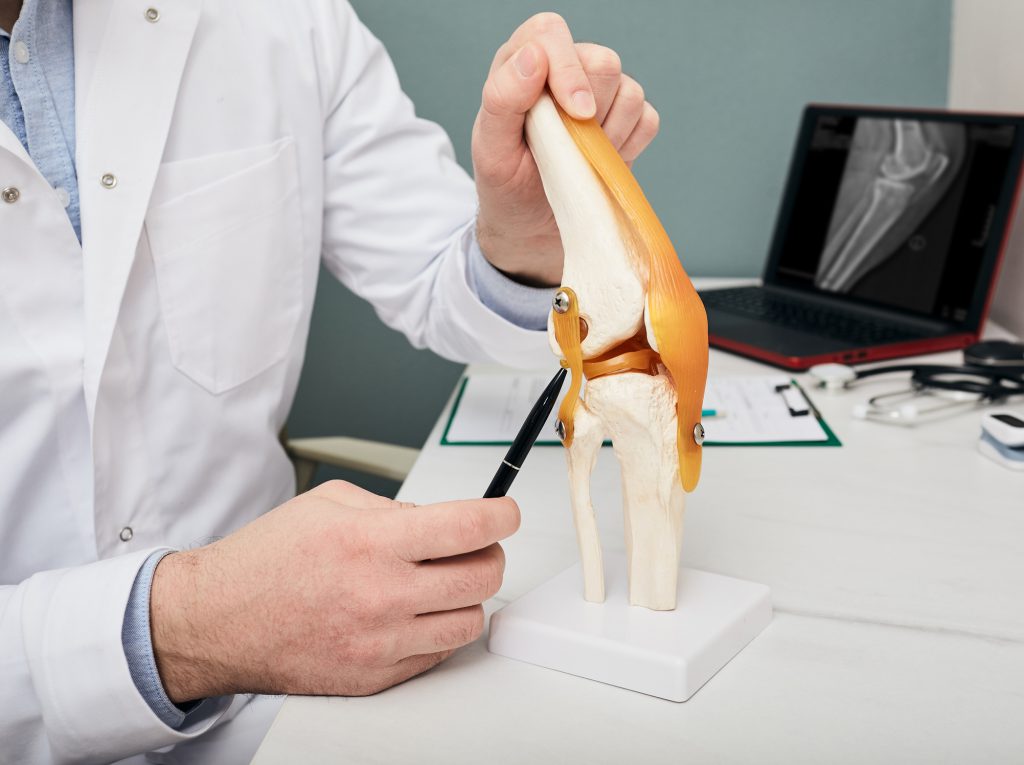
With school in full swing and more children participating in team sports, it is important to talk about injuries that can happen during physical activity. Some of these injuries involve damage to ligaments, which are pieces of connective tissue that connect two bones together.
The anterior cruciate ligament, known as the ACL, is the most injured knee ligament with approximately 100,000 – 200,000 ACL tears occurring each year in the United States.
ACL injuries happen most during sudden, cutting or pivoting movements which are common in sports such as soccer, basketball, and football.
Although anyone can injure their ACL, there are several factors that can place an individual at a greater risk. Risk factors include:
- Participating in the aforementioned sports, as well as lacrosse, skiing, tennis and gymnastics
- A previously torn ACL
- Being female (Females are more likely to get injured than males due to differences in anatomy)
- Poor conditioning
- Wearing poor fitting footwear
Most patients who experience an ACL tear report hearing a pop at the time of injury. Other symptoms can include severe pain or tenderness, swelling and knee instability with walking or a loss of range of motion (Squatting and walking downstairs are particularly difficult movements after obtaining an ACL tear).
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms following an injury to the knee, it is important that you see a doctor immediately.
When you arrive at your doctor, they will ask you for details about how the injury occurred. They will then examine the injured knee by comparing it to the uninjured knee. During the exam, your doctor may perform tests such as the Lachman and Anterior Drawer test to help determine if the ACL was damaged. Several imaging studies such as an x-ray may be ordered to see if there are associated fractures of the surrounding bones. An MRI may also be required to assess damage to soft tissue and check the extent of the ACL tear.
As with many injuries, acute management begins with RICE therapy which stands for rest, ice compression, elevation. If the knee appears unstable, crutches may be provided. A specially fitted brace may be another option to help stabilize the knee. Over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen can help control the pain. Further treatment options may include physical therapy or surgery.
ACL tears can be prevented by performing stretching and strengthening exercises that focus on the lower body and core, warming up before playing sports, as well as participating in year-round training and conditioning.
If you suspect that you or your loved ones may have injured your ACL or have incurred any other type of injury, our physicians at the Family Medicine Clinic would be happy to evaluate you and discuss a treatment plan based on your goals.
To schedule an appointment with one of our incredible physicians please call our office at (718) 657 -7093.

All content of this newsletter is intended for general information purposes only and is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Please consult a medical professional before adopting any of the suggestions on this page. You must never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment based upon any content of this newsletter. PROMPTLY CONSULT YOUR PHYSICIAN OR CALL 911 IF YOU BELIEVE YOU HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY.
